ECG
ECG is the process of creating an electrocardiogram, an electrocardiogram is a recording of heart activity through several cardiac cycles. It is an electrogram of the heart in which it is a graph of voltage versus time of electrical activity of the heart that uses electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes record small electrical changes that are brought about by cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cycle.
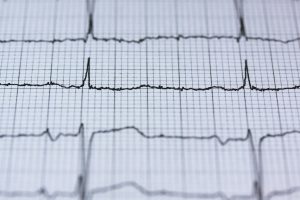 Traditionally, ECG usually refers to a 12-lead ECG performed lying down, as explained below. Other devices can, however, record the electrical activity of the heart, for example, a Holter monitor, and some smartwatches can record an ECG. ECG signals can be recorded in other settings with other devices.
Traditionally, ECG usually refers to a 12-lead ECG performed lying down, as explained below. Other devices can, however, record the electrical activity of the heart, for example, a Holter monitor, and some smartwatches can record an ECG. ECG signals can be recorded in other settings with other devices.
In a standard 12-lead ECG, ten electrodes are placed on the patient’s limbs and the surface of the chest. The overall magnitude of the heart’s electrical potential is then measured from twelve different angles and is recorded over some time usually ten seconds. In this way, the overall magnitude and direction of the heart’s electrical depolarization are captured at each moment throughout the cardiac cycle.
Medical uses
This can be viewed as an overarching purpose behind an ECG to glean information related to the heart’s electrical activity. While medical practice for this purpose can take many different forms, a quite common occurrence is that of needing the information to be combined with knowledge of the structure of the heart and physical examination signs to help interpret it.
Other common indications of the reason for the electrocardiogram include Chest pain or suspected myocardial infarction heart attack, such as ST elevated myocardial infarction and non-ST elevated myocardial infarction.
Shortness of breath, murmurs, syncope, seizure, funny turns, arrhythmias, new onset of palpitations, monitoring of known cardiac arrhythmias.
Drug monitoring, for example, drug-induced QT prolongation, digoxin toxicity, and management of overdose such as tricyclic overdose.
Monitoring of a patient throughout the perioperative period with any form of anesthesia like monitored anesthesia care, or general anesthesia. Preoperative evaluation and intraoperative and postoperative monitoring.

Protect
There is insufficient evidence to recommend using ECGs for adults without symptoms or at low risk of cardiovascular disease as a form of prevention. This is because an ECG may yield a false indication of a problem and thereby lead to misdiagnosis, recommendation of invasive procedures, and overtreatment. However, those who work on some very sensitive jobs like pilots might be required to carry out an ECG during their annual checkup. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy screening may also be carried out on athletes during sports physicals because of the possible sudden death that might occur.
ECG Tool
ECGs are done by machines that are essentially a combination of electrodes connected to the central unit. The first electrocardiographs were built with analog electronics in them, the signal was driving a motor to print the signal onto paper. Current electrocardiographs nowadays are using analog-to-digital converters, wherein this electrical activity of the heart is then converted into a digital signal. Most electrocardiographs today are portable devices. They can easily fit a screen, keyboard, and even a printer into a compact wheeled cart. In the present times, newer development includes designing even smaller versions to fit fitness trackers and smartwatches.
Cardiac Scanner
Beyond the traditional electrocardiograph machine, other recording devices are also in place. The idea of portable devices dates back to the origin of the Holter monitor in 1962. Traditionally, these were done by electrodes with patches attached to the skin to record ECG, but today, several devices can be put directly onto the chest as a patch with no attached wires and were proposed by Zio, TZ Medical, Philips, BardyDx, and so many more. These include the artificial cardiac pacemaker and the implantable cardioverter-defibrillator that can measure a far-field signal between the leads in the heart and the implanted battery/generator that resembles an ECG signal.
Lead Site on an ECG Report
A standard 12-lead ECG report and electrocardiograph show a 2.5-second find of each of the twelve leads. The tracings are most often in the configuration of four columns by three rows. The left column includes the limb leads I, II, and III, the middle column represents the augmented limb leads, and the last two columns contain the precordial leads. Alternatively, the electrocardiograph can present with an additional row on a rhythm strip, typically at the bottom as the fourth or fifth row.
Charge and rhythm
The sinoatrial node is the source of depolarization of the heart, and its rate of depolarization gives the heart rate in a normal heart. Like other vital signs, blood pressure, and respiratory rate, heart rate varies with age. The normal heart rate of an adult falls between 60 and 100 bpm, but it is higher in children. If below normal, it is known as bradycardia.
Above the normal range, it is called tachycardia. Yet another complication arises when the atria and ventricles of the heart are not coordinated therefore, the rate must also be specified as being either an atrial or a ventricular rate. For example, in ventricular fibrillation, the ventricular rate is 300–600 bpm, while the atrial rate might be normal or faster.
Ischemia and bar
ST-elevation myocardial infarctions have characteristic ECG findings that differ with the time elapsed since the MI first occurred. The initial sign is hyperacute T waves, peaked T waves resulting from local hyperkalemia in ischemic myocardium. Over minutes, this evolves to an elevation of the ST segment by at least 1 mm. Over hours, a pathologic Q wave may appear and the T wave will invert. The ST elevation will resolve over days. Pathologic Q waves usually will remain permanently.
Antique
Motion by the patient will distort an ECG tracing. Some rhythmic movements like shivering or tremors may create an illusion of a cardiac arrhythmia. Artifacts are distorted signals produced by secondary internal or external sources such as movement by muscles or interference by some electrical device.
Distortion is one challenge that health care providers use several techniques and strategies to allow them to safely recognize such false signals. The correct distinction between the ECG artifact and the true ECG signal may have a favorable effect on patient outcomes or liability in court.
CONCLUSION
There are many diagnoses made through ECG, as discussed above. Overall, the diagnosis is made based on the patterns. For example, an irregularly uneven QRS complex without P waves is the hallmark of atrial fibrillation however, other findings can be present as well, such as a roll branch block that alters the shape of the QRS complexes.
ECGs can be interpreted in isolation but should be tried like all diagnostic tests in the context of the patient. For example, peaked T waves are only an observation and are not diagnostic of hyperkalemia the diagnosis is confirmed by measuring the blood potassium level. Conversely, a finding of hyperkalemia should prompt an ECG for the expression of peaked T waves, widened QRS complexes, and loss of P waves. The following is a systematic list of potential diagnoses on ECG.
