Blood pressure
Blood pressure refers to the force that is applied by circulating blood to the blood vessel walls. The force that is created is a majority of the pressure put upon the body by the pumping heart to circulate the blood around the body—sometimes referred to simply as a brachial artery, more commonly though it refers to arterial blood pressure.
It is commonly measured as systolic pressure-maximum pressure in one heartbeat over diastolic pressure-minimum pressure between two heartbeats in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in milli of mercury above mmHg the surrounding atmospheric pressure, or in kilopascals kPa. The difference of pressure between systolic and diastolic is defined as pulse pressure while pressure found at an average time throughout the cardiac cycle is mean arterial pressure.

Forms of blood pressure
High blood pressure
The condition is sometimes referred to as hypertension, meaning a chronic medical condition that is marked by persistent elevation of BP in the arteries. Symptoms may not be caused by hypertension itself, but it forms the biggest risk factor for several conditions. These may consist of coronary artery disease and stroke, heart failure and atrial fibrillation as well as peripheral arterial diseases, vision loss, chronic kidney disease, and eventually dementia. Hypertension is one of the global killers.
Symptoms and signs
The symptoms of hypertension are relatively uncommon. The sufferer is unaware of their condition in half of all cases. This is typically discovered during a routine preventive care visit or as the reason for seeking care for another condition.
Some individuals have headaches, dizziness, vertigo, tinnitus buzzing, hissing in the ears, changes in vision, and fainting. These symptoms can be a manifestation of anxiety rather than hypertension.
Long-standing untreated hypertension may lead to organ damage that, in turn, causes features such as changes in the optic fundus, observable on ophthalmoscopy. The severity of hypertensive retinopathy usually directly correlates with the duration or the severity of the hypertension. Other organs affected as a result of hypertension are chronic kidney disease and enlargement of the heart muscle.
causes of hypertension
Depression is also associated with hypertension and loneliness is another risk factor. Periodontal disease has been associated with high blood pressure. Drinking water exposure to arsenic is also associated with elevated BP. Air pollution is associated with hypertension. Whether the above associations are causal, unknown. Gout and high blood uric acid are associated with hypertension and genetic Mendelian Randomization studies along with clinical trials, have indicated that this association is likely to be causal.
Early-life exposures including low birth weight, maternal smoking, and failure to breastfeed are thought to augment the risk for adult essential hypertension the associations are weak and mechanisms whereby these exposures may cause adult hypertension are unclear.

Lower blood pressure
Low blood pressure is a cardiovascular disorder wherein the BP of the arteries falls abnormally. This is the pressure exerted by the flow of blood against the artery walls during the pumping process of blood out of the heart, and it comes in the form of two figures. which are systolic BP at the top number or diastolic blood pressure at the bottom number. This measures the peak and trough in blood pressure within the cycle of cardiac activity. High pressure of less than 90 mmHg or a low pressure of less than 60 mmHg is hypotension. The values of children are different.
It becomes low only when it causes evident symptoms.
Signs of hypotension
Low blood pressure is generally asymptomatic. Hypotension may represent an underlying health condition when it develops acutely or in the setting of symptoms. Older adults are also at greater risk for symptoms of low BP, such as falls, syncope, or lightheadedness when rising or after meals. If the blood pressure is sufficiently low, syncope may become fainting.
This form of Low BP is associated with the following symptoms, many that are related to causes, not effects of hypotension: confusion, dizziness, feeling tired, weak, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, that sometimes feels like the heart, skipping beats, or even fluttering and chest pains.
Causes of Hypotension
Low blood pressure is caused by several factors, including low blood volume in the body, hormonal change, pregnancy, dilation of the blood vessels, medicine, severe dehydration, anemia, vitamin B12 deficiency, anaphylaxis, heart problems, and endocrine problems.
The most common cause of hypotension is a reduced blood volume and hypovolemia. It may be caused by hemorrhage or a decreased fluid intake, such as starvation or excessive fluid loss from diarrhea or vomiting. An overuse of diuretics is also a common cause of hypovolemia. Low BP can also be caused by heat stroke that may be shown by lack of perspiration, dizziness, and dark urine.
Some herbal medicines are reported to be hypotensive, that is, lower blood pressure and may interact with various drugs. Theobromine in Theobroma cacao is vasodilator and also a diuretic that lowers BP. It has been used to treat high BP.
Measurement of blood pressure
Most frequently used for measuring arterial pressure is a sphygmomanometer, which measures through auscultation and makes use of a column of height or mercury of an aneroid gauge. The most generally utilized methods of measurement are for automation of measurement of BP using the oscillometric method. Fully automated measurement using oscillometry was established in 1981. Even this principle is used for measuring blood pressure with a smartphone.
This refers to the far less frequent penetration of the arterial wall to make the measurement invasively. It is mainly used from within the confines of a hospital. The newest modern developments comprise research in developing newer methods that do not employ pressure appliances which work on direct interference with the human body of a patient while, at the same time, allowing for the measuring of blood pressure with no invasive nature, penetrating of the arterial wall as well as without the utilization of a cuff only employing optical sensors.
In office BP measurement, terminal digit preference occurs. One study reported that 40% of all recorded measurements had the last digit as zero, whereas in an unbiased situation, 10%–20% of the measurements should end in zero.
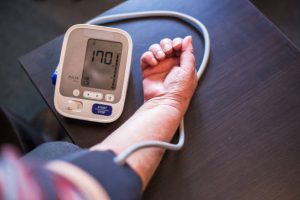
Keep your blood pressure in the normal range without medication
Reduce excess weight
In general, your blood pressure goes up as you gain weight. If you are overweight, you are also likely to stop breathing momentarily many times at night. This is called sleep apnea. Sleep apnea increases your blood pressure as well.
A considerable quantity of even a slight amount of loss of weight leads to weight loss as the best treatment of high blood pressure. A drop in BP often occurs if the person involved suffers from obesity or overweight cases. Blood pressure level is denoted in terms of millimeter mercury or simply mm Hg. By losing each kilogram weight approximately equivalent to 2.2 pounds, usually about1 mm Hg is noticed during such loss.
Do exercise on regular bases
Regular aerobic exercise can lower high blood pressure by about 5 to 8 mm Hg. Be consistent with your exercise since stopping it may lead the BP to rise up again. It is recommended to work out for at least half an hour a day. many people suffer from headaches, dizziness, vertigo, tinnitus buzzing, vision changes, and fainting spells due to hypertension.
Exercise also helps prevent BP that is a little above ideal from becoming elevated BP, also known as hypertension. For those diagnosed with hypertension, exercising regularly lowers blood pressure to safer levels.
Healthy food
A diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products and low in saturated fat and cholesterol can reduce high BP by as much as 11 mm Hg.
Intake of potassium through diet can minimize the effects of table salt and sodium on diet and BP. Processed food also contains added sodium by the food manufacturer to provide a salty flavor. The recommended daily amount is 3,500 to 5,000 milligrams mg. This will decrease BP by 4 to 5 mm Hg.
